
决战前端算法 — 树结构基础 — 堆与优先队列
发布于2021-05-30 07:07 阅读(1810) 评论(0) 点赞(18) 收藏(3)
本系列索引
堆与优先队列定义
在二叉树一文中讲到了完全二叉树,在这里复习一下完全二叉树的概念
完全二叉树是只允许最后一层右侧有空的二叉树,其有如下性质:
- 编号为 i 的节点(i=1开始),其左孩子节点编号为
2
∗
i
2*i
2∗i,其右孩子编号为
2
∗
i
+
1
2*i+1
2∗i+1
若 i 从0开始,则其左孩子节点编号为 2 ∗ i + 1 2*i+1 2∗i+1,其右孩子编号为 2 ∗ i + 2 2*i+2 2∗i+2 - 基于第一条性质,完全二叉树可以用数组来表示
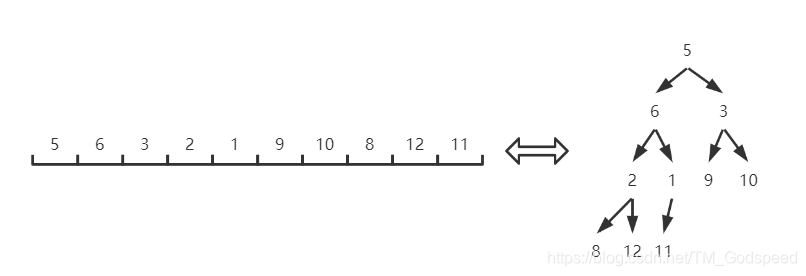
堆 就是通过完全二叉树实现的,通常将堆分为大顶堆和小顶堆
大顶堆
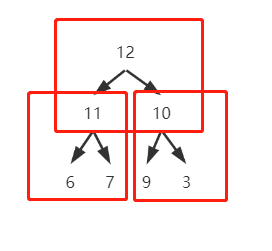
上图为一个简单的大顶堆,其有以下特点:
- 任意子顶堆的父节点的值比子节点的都大
- 堆只维护上下关系,也就是说次大值在第二层,第三大值可能在第二层或第三层,第四大值可能在2、3、4层,以此类推;换一个角度来说,只有父子间能比较大小,兄弟间比较不了
小顶堆
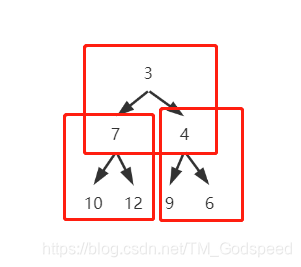
上图为一个简单的小顶堆,性质类比大顶堆
优先队列
回顾一下队列的性质,队列是一种先进先出的数据结构,最常用的是 push 和 pop 两个方法,而堆也有这两个方法。
不同的是,堆 pop() 出来的元素是整个堆元素中的最值,比如大顶堆依次把数据吐出来之后得到的是一个有序的降序序列,因此堆也被称作优先队列,依据此性质我们可以解决和有关维护最值的问题。
堆的实现方式
上文提到过,根据完全二叉树的性质我们可以将堆用数组的方式实现
- pop()
弹出数组首位元素,将原数组的最后一位进行数组头部的部位,然后进行下沉以维护堆的性质 - push()
在数组的最后一位推入元素,然后对数组的最后一位进行上浮以维护堆的性质
性质维护
- 上浮
找到当前节点的父节点并进行比较,以小顶堆举例,如果当前节点的值比父节点的值小,说明要进行交换(如果条件不符合,退出遍历) - 下沉
找到当前节点的左右子节点,以小顶堆举例,先标记当前节点,然后和左子节点比较,如果左子节点的值比当前节点小则标记该左子节点,如果右子节点的值比标记点小则标记右子节点,最后交换标记节点和当前节点(如果左右子节点都不符合要求,则退出遍历)
class Heap {
public heap: number[]
private readonly kind: boolean
constructor(arr: number[], kind: 'big' | 'small') {
this.kind = kind === 'big'
this.heap = arr
this.init()
}
private init() {
for (let i = 1; i < this.heap.length; i++) this.sortUp(i)
}
size() {
return this.heap.length
}
peek() {
return this.size() ? this.heap[0] : null
}
push(n: number) {
this.heap.push(n)
this.sortUp(this.heap.length - 1)
}
pop() {
if (!this.heap.length) return null
if (this.heap.length === 1) return this.heap.pop()
const res = this.heap[0]
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop()
this.sortDown(0)
return res
}
private sortUp(index: number) {
let parentIndex: number
while (index > 0) {
parentIndex = (index - 1) >> 1
if (this.kind) {
// 大顶堆
if (this.heap[parentIndex] < this.heap[index]) this.swap(index, parentIndex)
else break
} else {
// 小顶堆
if (this.heap[parentIndex] > this.heap[index]) this.swap(index, parentIndex)
else break
}
index = parentIndex
}
}
private sortDown(index: number) {
let leftIndex: number, rightIndex: number, target = index
while (index < this.heap.length - 1) {
leftIndex = (index << 1) + 1
rightIndex = (index << 1) + 2
if (this.kind) {
// 大顶堆
if (leftIndex < this.heap.length && this.heap[leftIndex] > this.heap[target]) target = leftIndex
if (rightIndex < this.heap.length && this.heap[rightIndex] > this.heap[target]) target = rightIndex
} else {
// 小顶堆
if (leftIndex < this.heap.length && this.heap[leftIndex] < this.heap[target]) target = leftIndex
if (rightIndex < this.heap.length && this.heap[rightIndex] < this.heap[target]) target = rightIndex
}
if (target === index) break
this.swap(target, index)
index = target
}
}
private swap(i: number, j: number) {
[this.heap[i], this.heap[j]] = [this.heap[j], this.heap[i]]
}
}
注意
获取父节点的时候代码使用了位运算,以下三种写法效果等同
parenIndex = (index - 1) >> 1
parenIndex = (index - 1) / 2 | 0
parenIndex = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2)
在初始化的时候,初始化操作是从头开始的,因为如果从尾开始,当遇到当前节点和父节点值相等时,就可能会使堆的性质被破坏
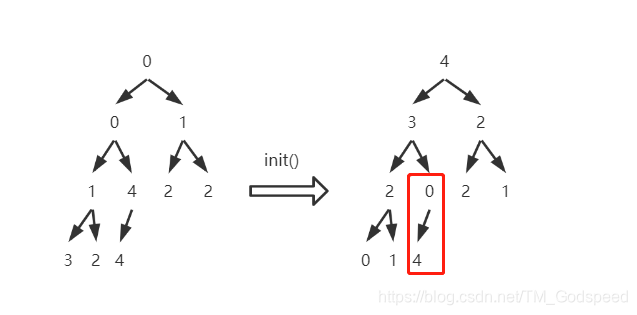
以上代码实现的堆的节点只是一个数字,但是在解决问题的时候,我们通常会使用更加复杂的数据结构,具体见以下习题
习题
在解决以下习题的时候,每次需要用到的堆我都会手动写一遍而不是单纯的复制粘贴。
刚学堆的时候我感觉这是我目前学过最简单的数据结构了,但是实际编写代码的时候出现了不少错误,有很多细节也只有错了之后才发现自己还有那么多细节没有掌握,所以读者希望能掌握这种数据结构的话,建议多写多练
当然有的时候堆并不是题目最优的解决方式,但是本文的习题都会尽量以堆来解决,因为本文的目的是练习堆的使用
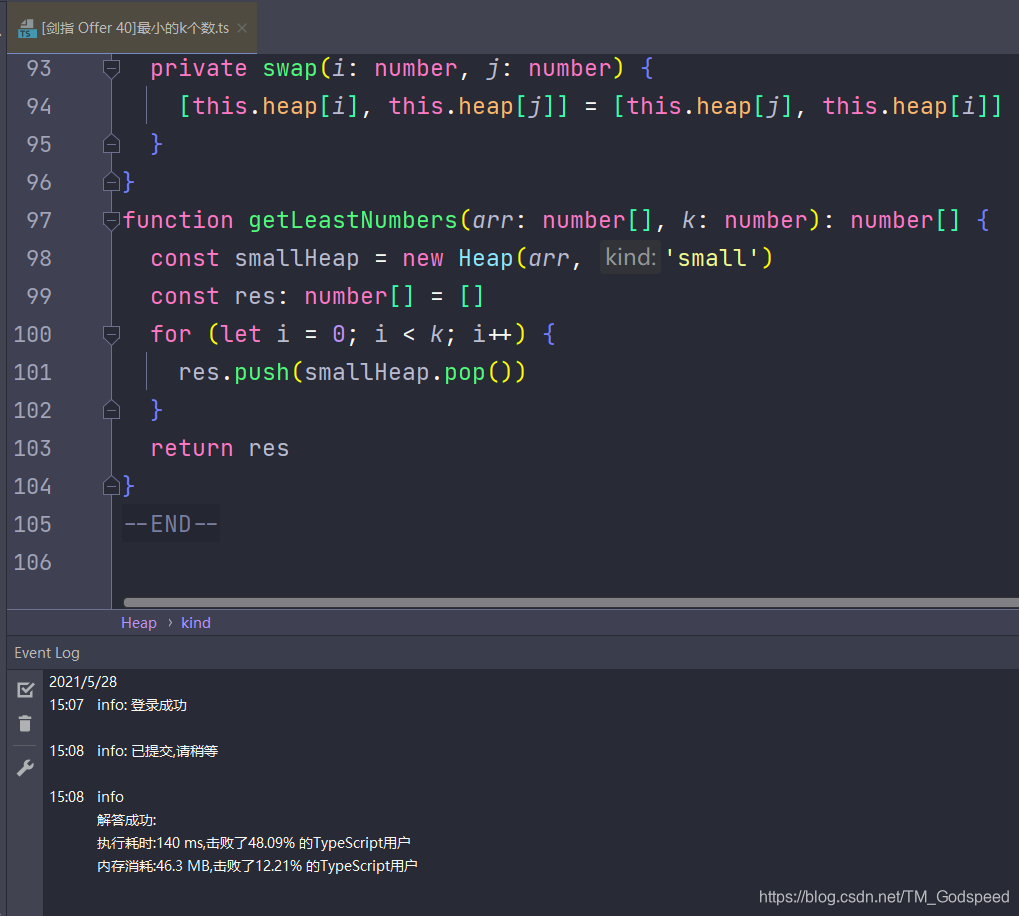
leetCode 剑指Offer 40 最小的k个数
看到“最”字,首先想到的就是堆维护最值的性质,所以这道题我们可以建一个小顶堆,前k个弹出的元素就是题目答案
class Heap {
public heap: number[]
private readonly kind: boolean
constructor(arr: number[], kind: 'big' | 'small') {
this.kind = kind === 'big'
this.heap = arr
this.init()
}
private init() {
for (let i = 1; i < this.heap.length; i++) this.sortUp(i)
}
push(n: number) {
this.heap.push(n)
this.sortUp(this.heap.length - 1)
}
pop() {
const res = this.heap.length ? this.heap[0] : null
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop()
this.sortDown(0)
return res
}
private sortUp(index: number) {
let parentIndex: number
while (index > 0) {
parentIndex = (index - 1) >> 1
if (this.kind) {
// 大顶堆
if (this.heap[parentIndex] < this.heap[index]) this.swap(index, parentIndex)
else break
} else {
// 小顶堆
if (this.heap[parentIndex] > this.heap[index]) this.swap(index, parentIndex)
else break
}
index = parentIndex
}
}
private sortDown(index: number) {
let leftIndex: number, rightIndex: number, target = index
while (index < this.heap.length - 1) {
leftIndex = (index << 1) + 1
rightIndex = (index << 1) + 2
if (this.kind) {
// 大顶堆
if (leftIndex < this.heap.length && this.heap[leftIndex] > this.heap[target]) target = leftIndex
if (rightIndex < this.heap.length && this.heap[rightIndex] > this.heap[target]) target = rightIndex
} else {
// 小顶堆
if (leftIndex < this.heap.length && this.heap[leftIndex] < this.heap[target]) target = leftIndex
if (rightIndex < this.heap.length && this.heap[rightIndex] < this.heap[target]) target = rightIndex
}
if (target === index) break
this.swap(target, index)
index = target
}
}
private swap(i: number, j: number) {
[this.heap[i], this.heap[j]] = [this.heap[j], this.heap[i]]
}
}
function getLeastNumbers(arr: number[], k: number): number[] {
const smallHeap = new Heap(arr, 'small')
const res: number[] = []
for (let i = 0; i < k; i++) {
res.push(smallHeap.pop())
}
return res
}
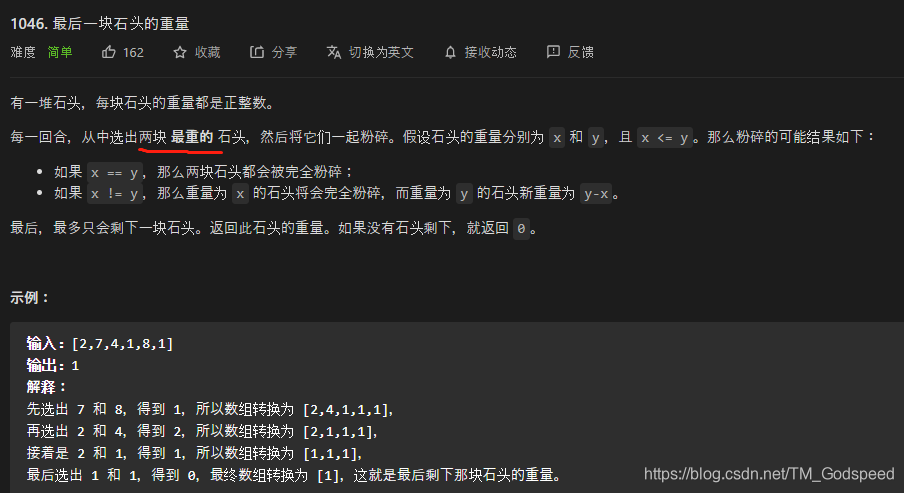
leetCode 1046 最后一块石头的重量
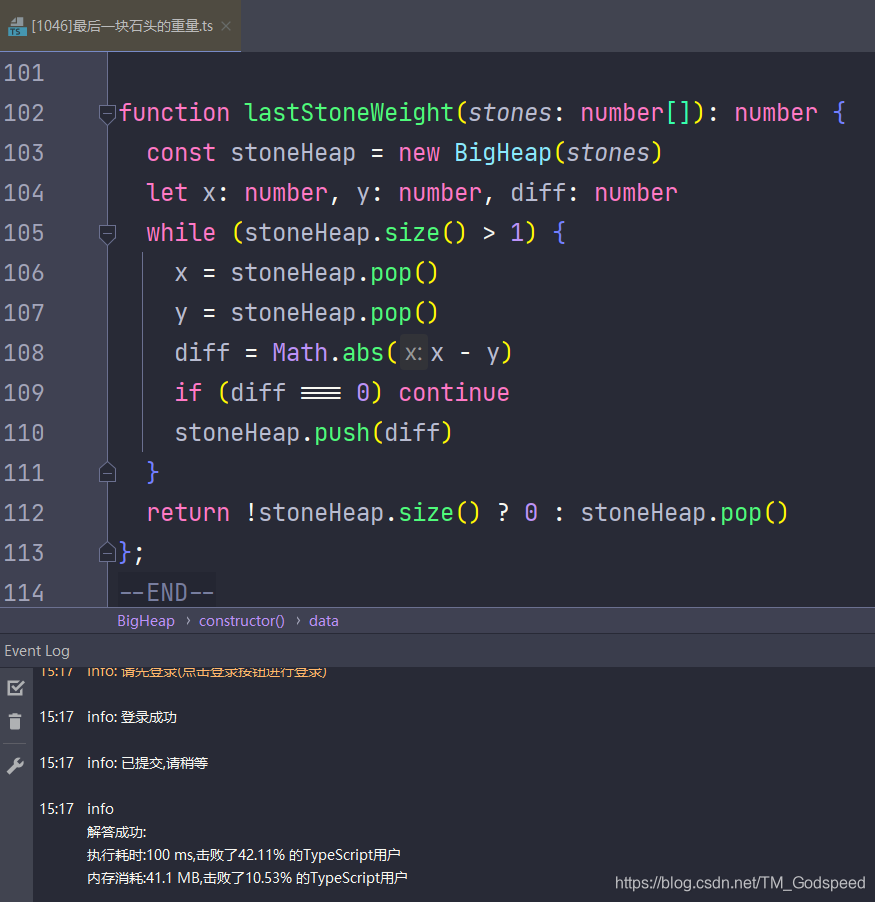
根据题目可知,我们需要一个大顶堆,每次取出两块石头进行操作,最后返回最后一块石头的重量,如果最后没有石头则返回0
class BigHeap {
public data: number[]
constructor(data: number[]) {
this.data = data
this.init()
}
init() {
for (let i = 1; i < this.data.length; i++) this.softUp(i)
}
size() {
return this.data.length
}
push(val: number) {
this.data.push(val)
this.softUp(this.data.length - 1)
}
pop() {
if (!this.data.length) return null
if (this.data.length === 1) return this.data.pop()
const res = this.data[0]
this.data[0] = this.data.pop()
this.softDown(0)
return res
}
softUp(index: number) {
let parentIndex: number
while (index) {
parentIndex = (index - 1) >> 1
if (this.data[parentIndex] < this.data[index]) {
this.swap(index, parentIndex)
index = parentIndex
} else break
}
}
softDown(index: number) {
let leftIndex: number, rightIndex: number, target: number
while (index < this.data.length) {
leftIndex = (index << 1) + 1
rightIndex = (index << 1) + 2
target = index
if (leftIndex < this.data.length && this.data[leftIndex] > this.data[target]) {
target = leftIndex
}
if (rightIndex < this.data.length && this.data[rightIndex] > this.data[target]) {
target = rightIndex
}
if (index === target) break
this.swap(index, target)
index = target
}
}
swap(i: number, j: number) {
[this.data[i], this.data[j]] = [this.data[j], this.data[i]]
}
}
function lastStoneWeight(stones: number[]): number {
const stoneHeap = new BigHeap(stones)
let x: number, y: number, diff: number
while (stoneHeap.size() > 1) {
x = stoneHeap.pop()
y = stoneHeap.pop()
diff = Math.abs(x - y)
if (diff === 0) continue
stoneHeap.push(diff)
}
return !stoneHeap.size() ? 0 : stoneHeap.pop()
}
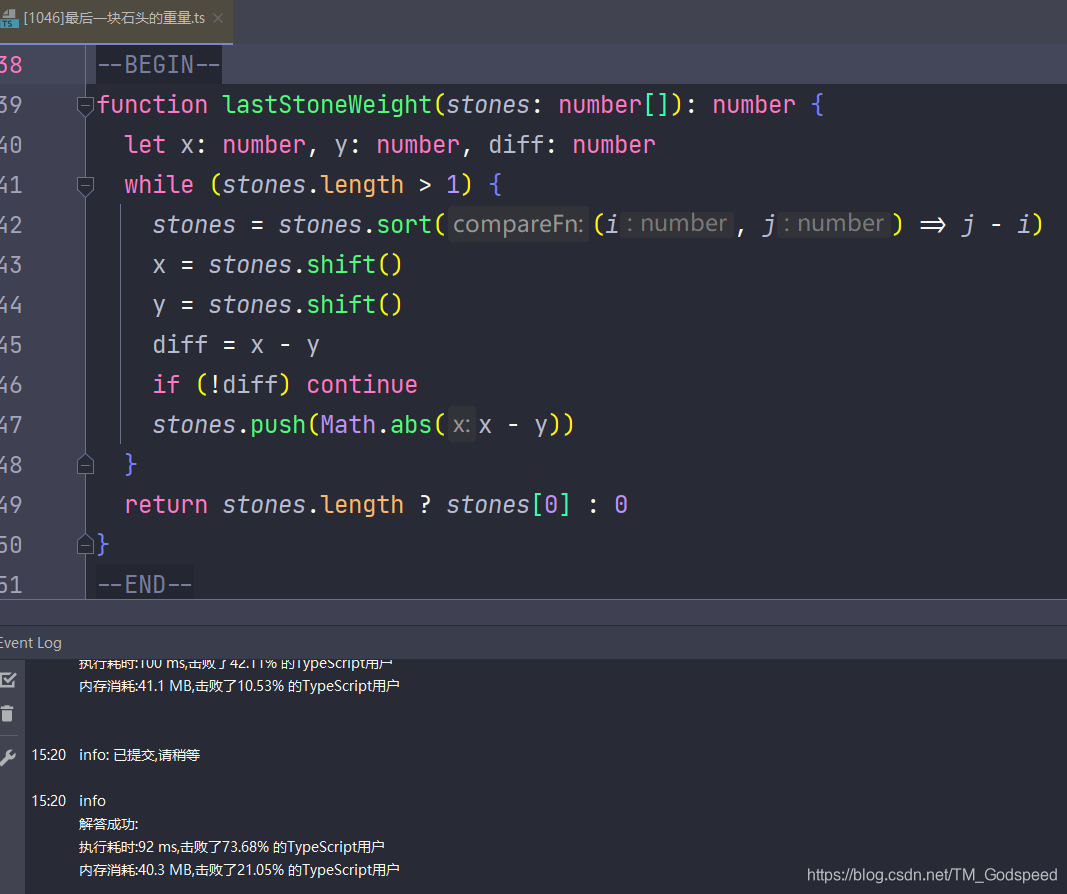
还有一种方法是通过 Array.sort() 对数组进行排序之后取出两个最大的元素进行操作,如此反复直到数组的长度小于2 (只剩一块石头或者没有石头)
function lastStoneWeight(stones: number[]): number {
let x: number, y: number, diff: number
while (stones.length > 1) {
stones = stones.sort((i, j) => j - i)
x = stones.shift()
y = stones.shift()
diff = x - y
if (!diff) continue
stones.push(Math.abs(x - y))
}
return stones.length ? stones[0] : 0
}
leetCode 703 数据流中的第k大元素
从题目可知,我们可以通过构建一个大顶堆,其吐出来的第k个元素即题目所求
注意这里的元素不能吐出来就丢了,得到结果之后还得让大顶堆吞回去
class BigHeap {
public data: number[]
constructor(data: number[]) {
this.data = data
this.init()
}
init() {
for (let i = 1; i < this.data.length; i++) this.sortUp(i)
}
peek() {
return this.data.length ? this.data[0] : null
}
push(val: number) {
this.data.push(val)
this.sortUp(this.data.length - 1)
}
pop() {
if (!this.data.length) return null
if (this.data.length === 1) return this.data.pop()
const res = this.data[0]
this.data[0] = this.data.pop()
this.sortDown(0)
return res
}
private sortUp(index: number) {
let parentIndex: number
while (index) {
parentIndex = (index - 1) >> 1
if (this.data[index] > this.data[parentIndex]) {
this.swap(index, parentIndex)
index = parentIndex
} else break
}
}
private sortDown(index: number) {
let leftIndex: number, rightIndex: number, target: number
while (index < this.data.length) {
target = index
leftIndex = (index << 1) + 1
rightIndex = (index << 1) + 2
if (leftIndex < this.data.length && this.data[leftIndex] > this.data[target]) target = leftIndex
if (rightIndex < this.data.length && this.data[rightIndex] > this.data[target]) target = rightIndex
if (target === index) break
this.swap(index, target)
index = target
}
}
private swap(i: number, j: number) {
[this.data[i], this.data[j]] = [this.data[j], this.data[i]]
}
}
class KthLargest {
private nums: BigHeap
private readonly k: number
constructor(k: number, nums: number[]) {
this.nums = new BigHeap(nums)
this.k = k
}
add(val: number): number {
const temp: number[] = []
this.nums.push(val)
for (let i = 0; i < this.k - 1; i++) {
temp.push(this.nums.pop())
}
const res = this.nums.peek()
const data = this.nums.data
this.nums = new BigHeap([...temp, ...data])
return res
}
}
这道题通过堆去做的话在提交的时候有一个测试用例没有通过,提示运行时间超出限制,这个也是堆的一个弊端,数据量一大的话处理起来就会特别费劲
在经过多次尝试后我依然没有找到优化方法以通过提交测试用例,所以这道题用堆的题解先写到这,大神们可以在评论区给出更优的解法
另外一种方法也是利用 Array.sort(),先让数组排好序再直接取
class KthLargest {
private nums: number[]
private readonly k: number
constructor(k: number, nums: number[]) {
this.nums = nums
this.k = k
}
add(val: number): number {
this.nums.push(val)
this.nums = this.nums.sort((i, j) => j - i)
return this.nums[this.k - 1]
}
}
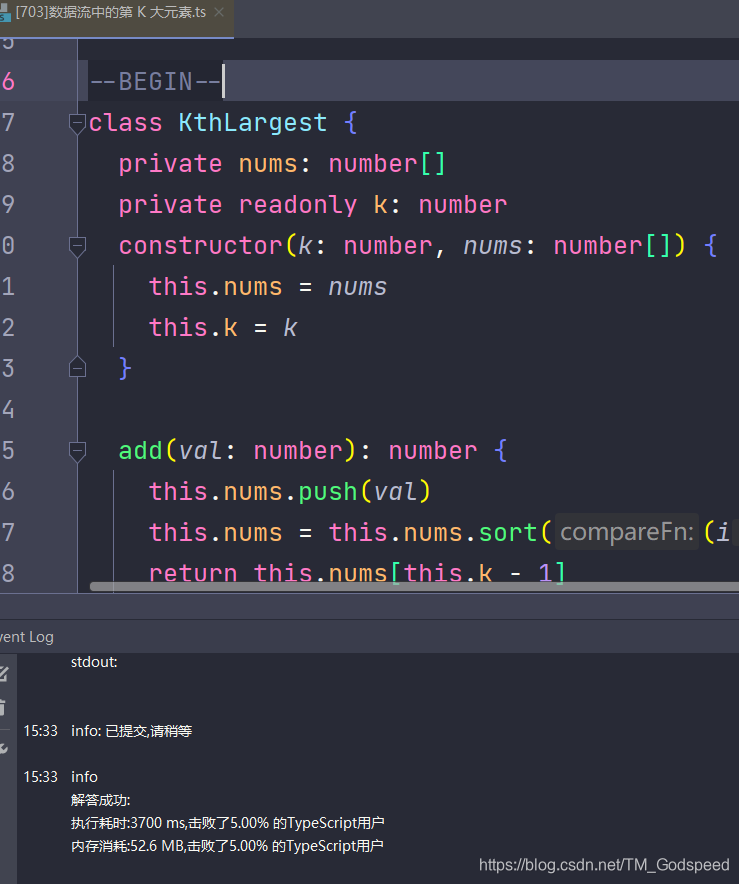
从提交结果来看原生的 sort() 在面对大量数据时表现出来的性能也一般,后面文章会介绍排序算法,希望大家能继续支持
leetCode 215 数组中的第k大元素
这道题可以用排序、大顶堆、小顶堆的方法解答
先介绍最简单的排序,使用排序的方法在函数中只要写1行代码即可
function findKthLargest(nums: number[], k: number): number {
return nums.sort((i, j) => j - i)[k - 1]
}
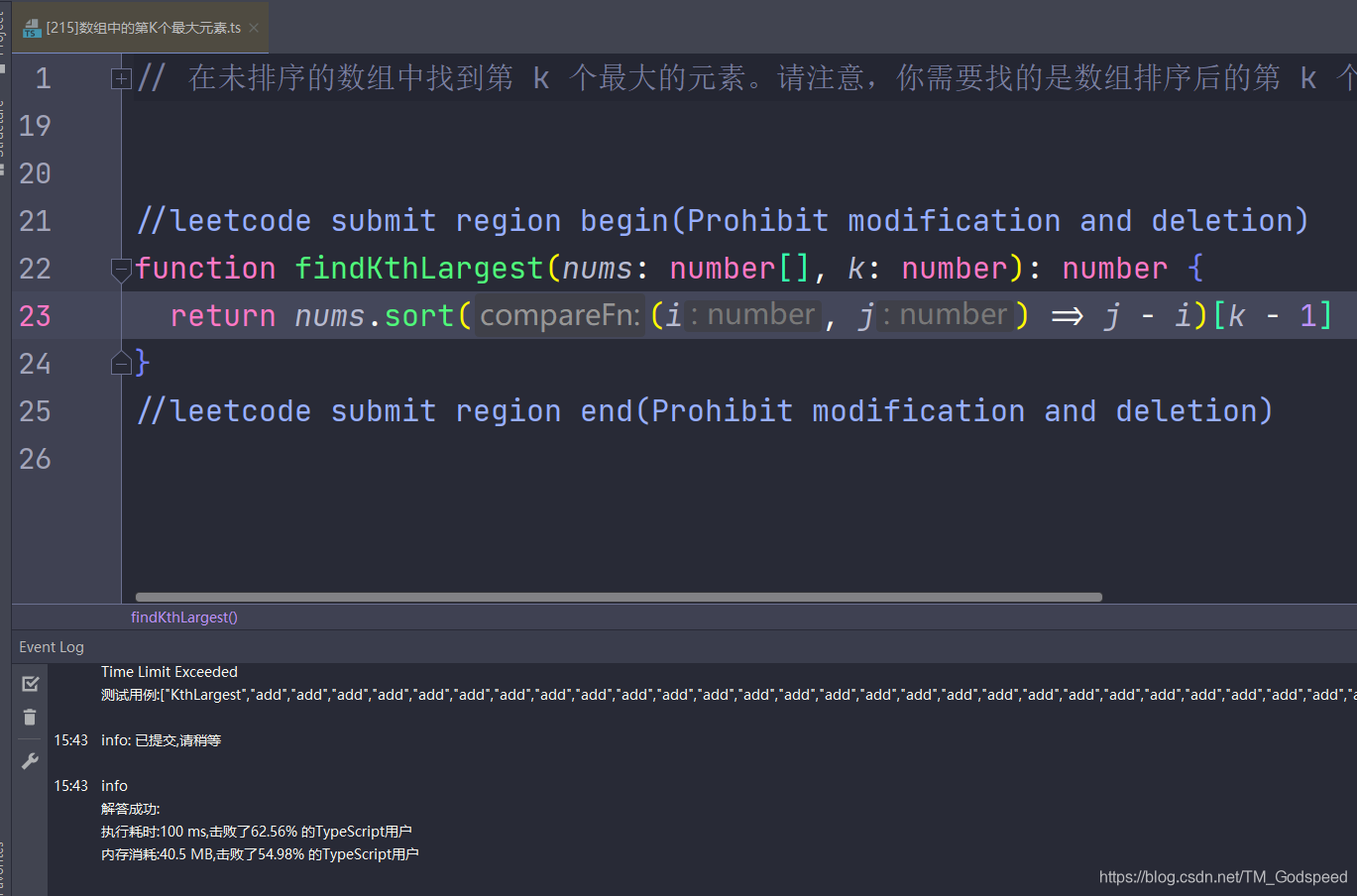
使用大顶堆的话只要弹
k
−
1
k-1
k−1 次堆,最后堆顶元素即题目所求
class Heap {
public data: number[]
private readonly kind: boolean
constructor(data: number[], kind: 'big' | 'small') {
// 为了能用小顶堆解题而使用了深拷贝
this.data = [...data]
this.kind = kind === 'big'
this.init()
}
private init() {
for (let i = 1; i < this.data.length; i++) this.sortUp(i)
}
peek() {
return this.data.length ? this.data[0] : null
}
size() {
return this.data.length
}
push(val: number) {
this.data.push(val)
this.sortUp(this.data.length - 1)
}
pop() {
if (!this.data.length) return null
if (this.data.length === 1) return this.data.pop()
const res = this.data[0]
this.data[0] = this.data.pop()
this.sortDown(0)
return res
}
private sortUp(index: number) {
let parentIndex: number
while (index) {
parentIndex = (index - 1) >> 1
if (this.kind) {
// 大顶堆
if (this.data[index] > this.data[parentIndex]) this.swap(index, parentIndex)
else break
} else {
// 小顶堆
if (this.data[parentIndex] > this.data[index]) this.swap(index, parentIndex)
else break
}
index = parentIndex
}
}
private sortDown(index: number) {
let leftIndex: number, rightIndex: number, target: number
while (index < this.data.length) {
leftIndex = (index << 1) + 1
rightIndex = (index << 1) + 2
target = index
if (this.kind) {
// 大顶堆
if (leftIndex < this.data.length && this.data[leftIndex] > this.data[target]) target = leftIndex
if (rightIndex < this.data.length && this.data[rightIndex] > this.data[target]) target = rightIndex
} else {
// 小顶堆
if (leftIndex < this.data.length && this.data[leftIndex] < this.data[target]) target = leftIndex
if (rightIndex < this.data.length && this.data[rightIndex] < this.data[target]) target = rightIndex
}
if (target === index) break
this.swap(target, index)
index = target
}
}
private swap(i: number, j: number) {
[this.data[i], this.data[j]] = [this.data[j], this.data[i]]
}
}
function findKthLargest(nums: number[], k: number): number {
const numsHeap = new Heap(nums, "big")
for (let i = 0; i < k - 1; i++) {
numsHeap.pop()
}
return numsHeap.peek()
}
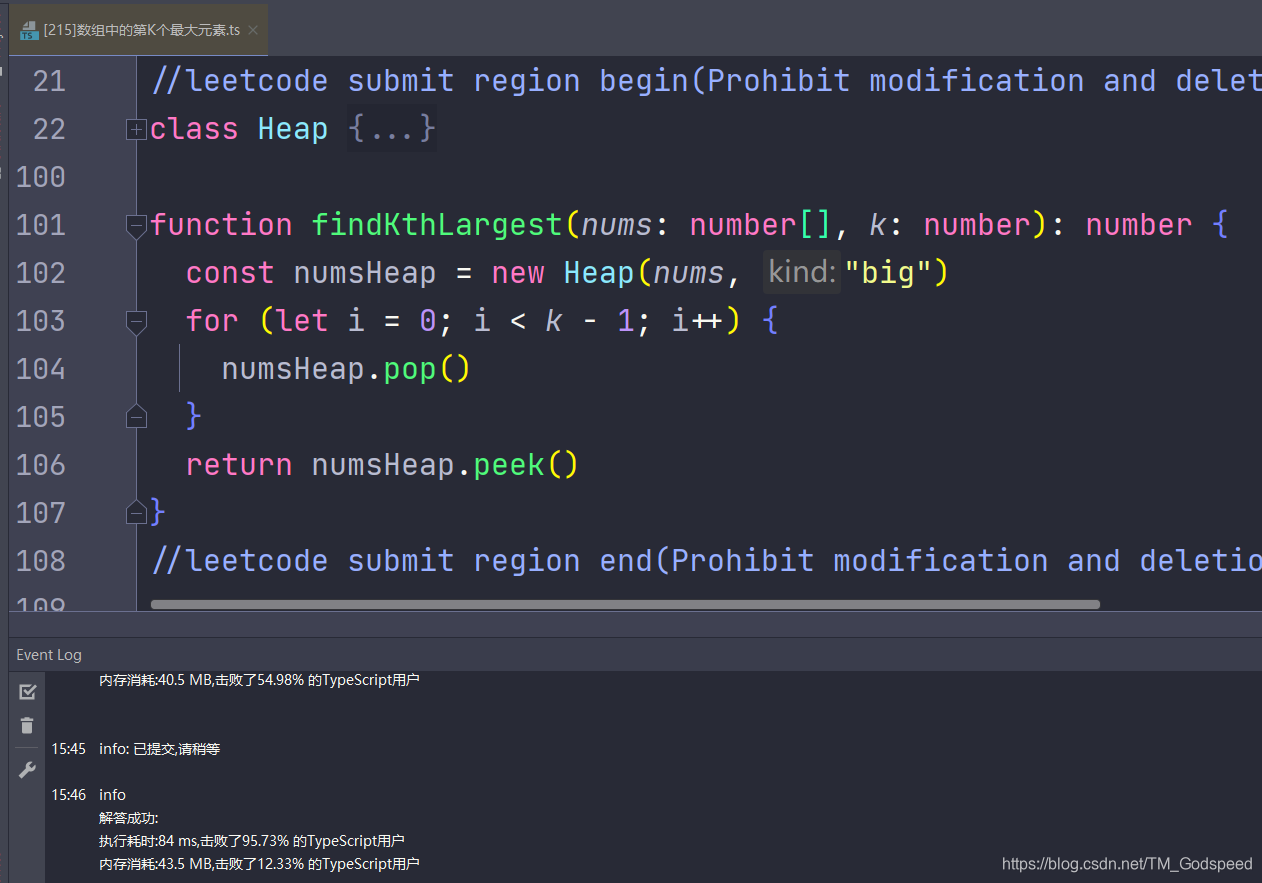
使用小顶堆的话只要弹
l
e
n
g
t
h
−
k
length-k
length−k 次堆,最后返回堆顶即题目所求
class Heap {
public data: number[]
private readonly kind: boolean
constructor(data: number[], kind: 'big' | 'small') {
// 为了能用小顶堆解题而使用了深拷贝
this.data = [...data]
this.kind = kind === 'big'
this.init()
}
private init() {
for (let i = 1; i < this.data.length; i++) this.sortUp(i)
}
peek() {
return this.data.length ? this.data[0] : null
}
size() {
return this.data.length
}
push(val: number) {
this.data.push(val)
this.sortUp(this.data.length - 1)
}
pop() {
if (!this.data.length) return null
if (this.data.length === 1) return this.data.pop()
const res = this.data[0]
this.data[0] = this.data.pop()
this.sortDown(0)
return res
}
private sortUp(index: number) {
let parentIndex: number
while (index) {
parentIndex = (index - 1) >> 1
if (this.kind) {
// 大顶堆
if (this.data[index] > this.data[parentIndex]) this.swap(index, parentIndex)
else break
} else {
// 小顶堆
if (this.data[parentIndex] > this.data[index]) this.swap(index, parentIndex)
else break
}
index = parentIndex
}
}
private sortDown(index: number) {
let leftIndex: number, rightIndex: number, target: number
while (index < this.data.length) {
leftIndex = (index << 1) + 1
rightIndex = (index << 1) + 2
target = index
if (this.kind) {
// 大顶堆
if (leftIndex < this.data.length && this.data[leftIndex] > this.data[target]) target = leftIndex
if (rightIndex < this.data.length && this.data[rightIndex] > this.data[target]) target = rightIndex
} else {
// 小顶堆
if (leftIndex < this.data.length && this.data[leftIndex] < this.data[target]) target = leftIndex
if (rightIndex < this.data.length && this.data[rightIndex] < this.data[target]) target = rightIndex
}
if (target === index) break
this.swap(target, index)
index = target
}
}
private swap(i: number, j: number) {
[this.data[i], this.data[j]] = [this.data[j], this.data[i]]
}
}
function findKthLargest(nums: number[], k: number): number {
const numsHeap = new Heap(nums, "small")
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length - k; i++) {
numsHeap.pop()
}
return numsHeap.peek()
}
leetCode 373 查找和最小的k对数字
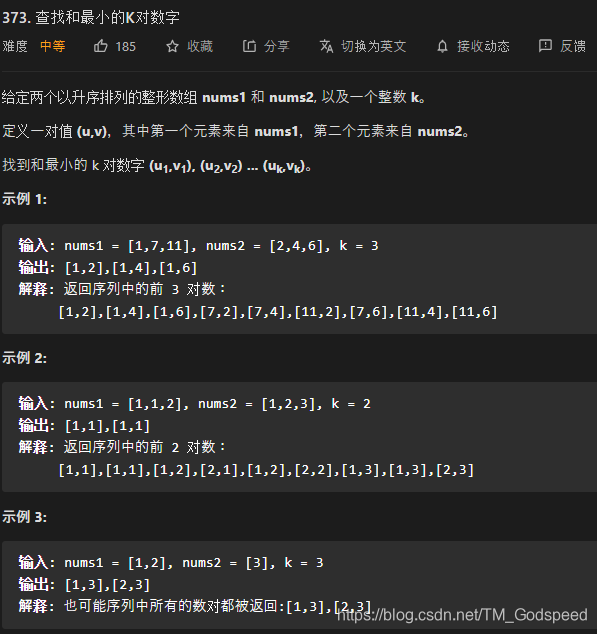
既然要找最小的元素,自然想到用小顶堆
当然本题不能像之前一样创建出来的堆的节点的数据类型是数字,在这里我定义节点的数据类型为 [[number, number], number]
第一个元素是一个数组,值为题目所提供的数字对;第二个元素是两个数字的和,进行上浮和下沉操作时比较的是节点的第二个元素
class SmallHeap {
public data: [[number, number], number][]
constructor(data: [[number, number], number][]) {
this.data = data
}
private init() {
for (let i = 1; i < this.data.length; i++) this.sortUp(i)
}
size() {
return this.data.length
}
push(val: [[number, number], number]) {
this.data.push(val)
this.sortUp(this.data.length - 1)
}
pop() {
if (!this.data.length) return null
if (this.data.length === 1) return this.data.pop()
const res = this.data[0]
this.data[0] = this.data.pop()
this.sortDown(0)
return res
}
private sortUp(index: number) {
let parentIndex: number
while (index) {
parentIndex = (index - 1) >> 1
if (this.data[index][1] < this.data[parentIndex][1]) {
this.swap(index, parentIndex)
index = parentIndex
} else break
}
}
private sortDown(index: number) {
let leftIndex: number, rightIndex: number, target: number
while (index < this.data.length) {
leftIndex = (index << 1) + 1
rightIndex = (index << 1) + 2
target = index
if (leftIndex < this.data.length && this.data[leftIndex][1] < this.data[target][1]) target = leftIndex
if (rightIndex < this.data.length && this.data[rightIndex][1] < this.data[target][1]) target = rightIndex
if (target === index) break
this.swap(index, target)
index = target
}
}
private swap(i: number, j: number) {
[this.data[i], this.data[j]] = [this.data[j], this.data[i]]
}
}
function kSmallestPairs(nums1: number[], nums2: number[], k: number): number[][] {
const smallHeap = new SmallHeap([])
nums1.forEach(n1 => nums2.forEach(n2 => smallHeap.push([[n1, n2], n1 + n2])))
const res: number[][] = []
while (k--) {
if (smallHeap.size()) res.push(smallHeap.pop()[0])
}
return res
}
leetCode 692 前k个高频单词
这道题可以使用大顶堆来解题,堆中节点的数据类型为 [string, number],第一个元素是单词,第二个单词是出现次数
这里的节点比较操作有两点,首先是比较出现次数,当出现次数相同时比较字符串,比较字符串的呃时候优先比较首字母的排序顺序,如果首字母相同则比较字符串长度,长度较小的优先
在 js 中字符串比较直接使用比较符号即可,其会按照上述规则进行比较
function topKFrequent(words: string[], k: number): string[] {
const counter: { [key: string]: number } = {}
const smallHeap: [string, number][] = []
words.forEach(word => counter[word] = counter[word] ? ++counter[word] : 1)
let i = 0
for (let key in counter) {
if (i < k) {
smallHeap.push([key, counter[key]])
if (i === k - 1) initHeap(counter, smallHeap, k)
} else if (counter[key] > smallHeap[0][1] || (counter[key] === smallHeap[0][1] && key < smallHeap[0][0])) {
smallHeap[0] = [key, counter[key]]
sortDown(counter, smallHeap, k, 0)
}
i++
}
const temp = smallHeap.sort((a, b) => {
if (a[1] > b[1]) return -1
else if (a[1] < b[1]) return 1
else {
if (a[0] > b[0]) return 1
else if (a[0] < b[0]) return -1
}
})
return temp.map(item => item[0])
}
function initHeap(map: { [key: string]: number }, arr: [string, number][], len: number) {
for (let i = len >> 1; i >= 0; i--) sortDown(map, arr, len, i)
}
function sortDown(map: { [key: string]: number }, arr: [string, number][], len: number, index: number) {
const leftIndex = (index << 1) + 1, rightIndex = (index << 1) + 2
let target = index
if (leftIndex < len && (
(map[arr[leftIndex][0]] < map[arr[target][0]]) ||
((map[arr[leftIndex][0]] === map[arr[target][0]]) && (arr[leftIndex][0] > arr[target][0]))
)) {
target = leftIndex
}
if (rightIndex < len && (
(map[arr[rightIndex][0]] < map[arr[target][0]]) ||
((map[arr[rightIndex][0]] === map[arr[target][0]]) && (arr[rightIndex][0] > arr[target][0]))
)) {
target = rightIndex
}
if (target !== index) {
swap(arr, target, index)
sortDown(map, arr, len, target)
}
}
function swap(arr: any[], i: number, j: number) {
[arr[i], arr[j]] = [arr[j], arr[i]]
}
leetCode 295 数据流的中位数
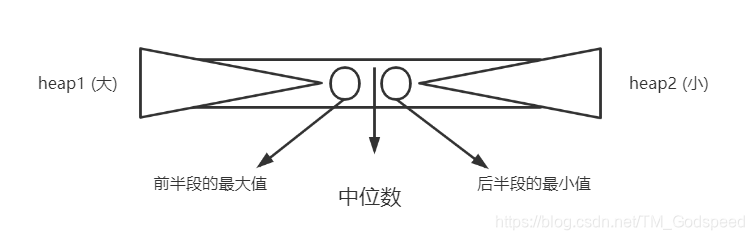
从上图可以发现,中位数的前一个数字是前半段的最大值,中位数的后一个数字是后半段的最小值,因此我们需要一个大顶堆维护前半段的数字,一个小顶堆维护后半段的数字
为了维护整个数列的有序性,在插入时我们需要以下规则
- h1为空或者当前加入值≤h1堆顶时往h1里推,否则往h2里推
- 使 h 1 数 量 ≥ h 2 数 量 + 1 h1数量≥h2数量+1 h1数量≥h2数量+1
- 当h1和h2的数量和为奇数时,中位数就是h1堆顶;
当h1和h2的数量和为偶数时,中位数就是两个堆顶和的平均值
class Heap {
public data: number[]
private readonly kind: boolean
constructor(data: number[], kind: 'big' | 'small') {
this.data = [...data]
this.kind = kind === 'big'
this.init()
}
private init () {
for (let i = 1; i < this.data.length; i++) this.sortUp(i)
}
size() {
return this.data.length
}
peek() {
return this.data.length ? this.data[0] : null
}
push(val: number) {
this.data.push(val)
this.sortUp(this.data.length - 1)
}
pop() {
if (!this.data.length) return null
if (this.data.length === 1) return this.data.pop()
const res = this.data[0]
this.data[0] = this.data.pop()
this.sortDown(0)
return res
}
private sortUp(index: number) {
let parentIndex: number
while (index) {
parentIndex = (index - 1) >> 1
if (this.kind) {
// 大顶堆
if (this.data[index] > this.data[parentIndex]) this.swap(index, parentIndex)
else break
} else {
// 小顶堆
if (this.data[index] < this.data[parentIndex]) this.swap(index, parentIndex)
else break
}
index = parentIndex
}
}
private sortDown(index: number) {
let leftIndex: number, rightIndex: number, target: number
while (index < this.data.length) {
leftIndex = (index << 1) + 1
rightIndex = (index << 1) + 2
target = index
if (this.kind) {
// 大顶堆
if (leftIndex < this.data.length && this.data[leftIndex] > this.data[target]) target = leftIndex
if (rightIndex < this.data.length && this.data[rightIndex] > this.data[target]) target = rightIndex
} else {
// 小顶堆
if (leftIndex < this.data.length && this.data[leftIndex] < this.data[target]) target = leftIndex
if (rightIndex < this.data.length && this.data[rightIndex] < this.data[target]) target = rightIndex
}
if (target === index) break
this.swap(target, index)
index = target
}
}
private swap(i: number, j: number) {
[this.data[i], this.data[j]] = [this.data[j], this.data[i]]
}
}
class MedianFinder {
public front: Heap
public last: Heap
constructor() {
this.front = new Heap([], 'big')
this.last = new Heap([], 'small')
}
addNum(num: number): void {
//* 1.推入添加数字
if (!this.front.size() || num <= this.front.peek()) this.front.push(num)
else this.last.push(num)
//* 2.平衡左右堆
if (this.front.size() > this.last.size() + 1) this.last.push(this.front.pop())
if (this.last.size() > this.front.size()) this.front.push(this.last.pop())
}
findMedian(): number {
const even = ((this.front.size() + this.last.size()) % 2) === 0
if (even) {
return (this.front.peek() + this.last.peek()) / 2
}
return this.front.peek()
}
}
扩展
我们可以通过调整前后堆的数量关系维护数据流的任意位置,比如前三分之一后三分之一的位置
leetCode 1753 移除石子的最大得分
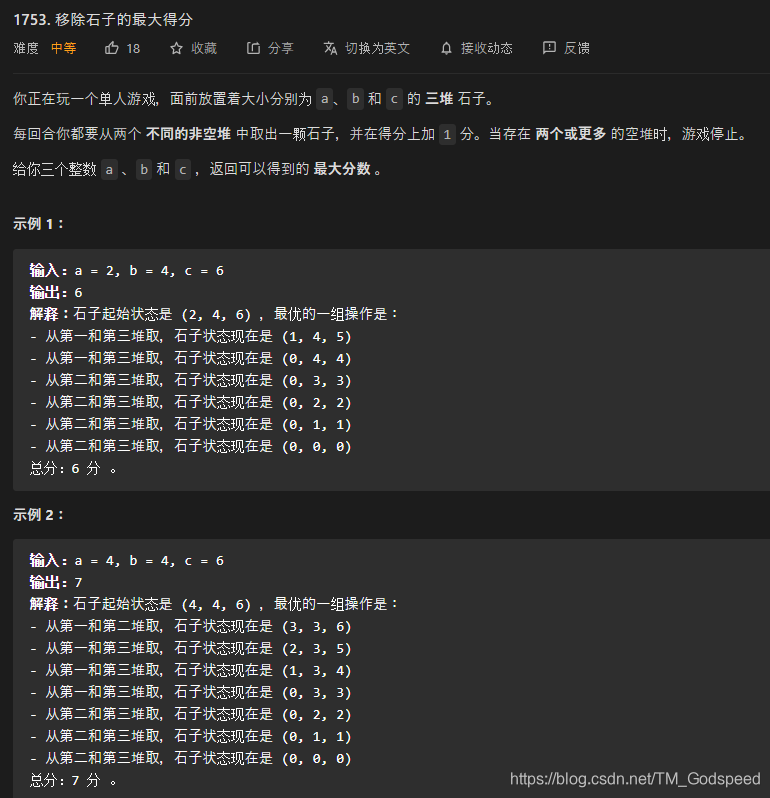
这道题其实就是一道脑筋急转弯的题目,这里给出的是一种解决方法,可能有其他解法
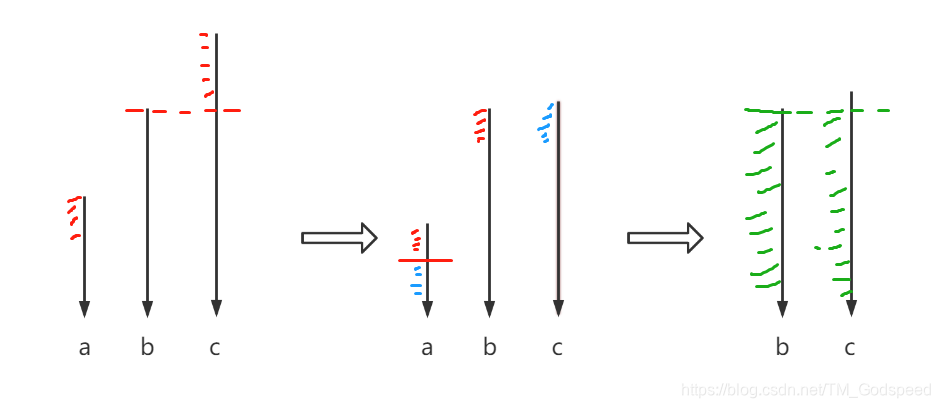
- 首先给三个石堆排序为有序递增
- 取c与b的差和a的最小值,得分增加该最小值,a减去该最小值(从逻辑上来看c也要减去该最小值,但是之后c就没用上,所以这里只要对a操作即可)
- 当a为奇数时自减1使其变成偶数,b、c平分a,得分加a,b减去a的一半
- 最后得分加b就是题目所求
上图并没有展示所有情况,但是所有情况经过上述步骤都能得到正解,读者想到其他情况的话可以套用上述步骤进行验证
function maximumScore(a: number, b: number, c: number): number {
let ans = 0
const sorted = [a, b, c].sort((a, b) => a - b)
const min = Math.min(sorted[0], sorted[2] - sorted[1])
ans += min
sorted[0] -= min
if (sorted[0] > 0) {
if (sorted[0] % 2 === 1) sorted[0]--
ans += sorted[0]
sorted[1] -= sorted[0] / 2
}
return ans + sorted[1]
}
leetCode 1801 积压订单的订单总数
这道题的题目比较复杂,这里简单解释一下
题目会给出两种订单类型,购买订单和销售订单,在这两种订单中会给出价格和数量,最后我们要求出没有处理的订单总数
处理订单的原则只有一个:购买价格要≥销售价格 (不能赔本)
利
润
=
购
买
价
格
−
销
售
价
格
利润=购买价格-销售价格
利润=购买价格−销售价格
为了使利益最大化,我们可以使用大顶堆来维护购买订单,使用小顶堆来维护销售订单
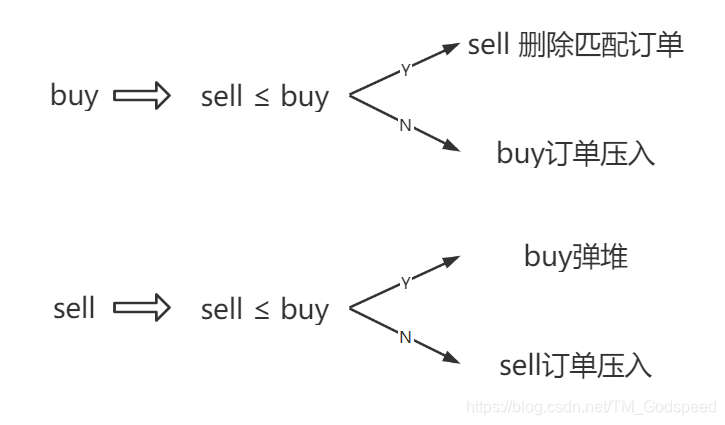
此题的堆的节点数据结构为 [number, number],第一个元素表示价格,第二个元素表示订单数,在维护堆的时候比较的是价格
class Heap {
// [价格, 订单数]
public data: [number, number][]
private readonly kind: boolean
constructor(data: [number, number][], kind: 'big' | 'small') {
this.data = data
this.kind = kind === 'big'
this.init()
}
private init() {
for (let i = 1; i < this.data.length; i++) this.sortUp(i)
}
size() {
return this.data.length
}
peek() {
return this.data.length ? this.data[0] : null
}
push(val: [number, number]) {
this.data.push(val)
this.sortUp(this.data.length - 1)
}
pop() {
if (!this.data.length) return null
if (this.data.length === 1) return this.data.pop()
const res = this.data[0]
this.data[0] = this.data.pop()
this.sortDown(0)
return res
}
private sortUp(index: number) {
let parentIndex: number
while (index) {
parentIndex = (index - 1) >> 1
if (this.kind) {
// 大顶堆
if (this.data[index][0] > this.data[parentIndex][0]) this.swap(index, parentIndex)
else break
} else {
// 小顶堆
if (this.data[index][0] < this.data[parentIndex][0]) this.swap(index, parentIndex)
else break
}
index = parentIndex
}
}
private sortDown(index: number) {
let leftIndex: number, rightIndex: number, target: number
while (index < this.data.length) {
leftIndex = (index << 1) + 1
rightIndex = (index << 1) + 2
target = index
if (this.kind) {
// 大顶堆
if (leftIndex < this.data.length && this.data[leftIndex][0] > this.data[target][0]) target = leftIndex
if (rightIndex < this.data.length && this.data[rightIndex][0] > this.data[target][0]) target = rightIndex
} else {
// 小顶堆
if (leftIndex < this.data.length && this.data[leftIndex][0] < this.data[target][0]) target = leftIndex
if (rightIndex < this.data.length && this.data[rightIndex][0] < this.data[target][0]) target = rightIndex
}
if (target === index) break
this.swap(index, target)
index = target
}
}
private swap(i: number, j: number) {
[this.data[i], this.data[j]] = [this.data[j], this.data[i]]
}
}
function getNumberOfBacklogOrders(orders: number[][]): number {
let res = 0, min = 0
const buy = new Heap([], "big")
const sell = new Heap([], 'small')
// 0 buy 1 sell
orders.forEach(([price, amount, orderType]) => {
if (orderType) {
// sell
while (amount) {
if (buy.size() && buy.peek()[0] >= price) {
min = Math.min(buy.peek()[1], amount)
buy.peek()[1] -= min
amount -= min
if (buy.peek()[1] === 0) buy.pop()
} else {
sell.push([price, amount])
break
}
}
} else {
// buy
while (amount) {
if (sell.size() && price >= sell.peek()[0]) {
min = Math.min(amount, sell.peek()[1])
sell.peek()[1] -= min
amount -= min
if (sell.peek()[1] === 0) sell.pop()
} else {
buy.push([price, amount])
break
}
}
}
})
// 处理积压订单
while (buy.size() && sell.size() && buy.peek()[0] >= sell.peek()[0]) {
min = Math.min(buy.peek()[1], sell.peek()[1])
buy.peek()[1] -= min
sell.peek()[1] -= min
if (!buy.peek()[1]) buy.pop()
if (!sell.peek()[1]) sell.pop()
}
while (buy.size()) res += buy.pop()[1]
while (sell.size()) res += sell.pop()[1]
return res % 1000000007
}
leetCode 355 设计推特
这道题要注意的是我们要维护一个用户列表,这个用户列表维护的是每个用户的关注和自己发的推特,注意每个用户的关注中必须有自己(这样可以在获取推特的时候更方便处理)
由于测试用例只能一条一条执行,所以我们可以定义一个整形的数字来记录推特发表的时间
使用大顶堆来维护最新发表的10条推特,这个大顶堆的节点的数据结构为 [number, number],第一个元素为推特id,第二个元素为推特发表时间,在维护堆的时候只要比较时间即可
class TweetsHeap {
// [tweetId, time]
public data: [number, number][]
constructor() {
this.data = []
}
size() {
return this.data.length
}
push(val: [number, number]) {
this.data.push(val)
this.sortUp(this.data.length - 1)
}
pop() {
if (!this.data.length) return null
if (this.data.length === 1) return this.data.pop()
const res = this.data[0]
this.data[0] = this.data.pop()
this.sortDown(0)
return res
}
clear () {
this.data = []
}
private sortUp(index: number) {
let parentIndex: number
while (index) {
parentIndex = (index - 1) >> 1
if (this.data[index][1] > this.data[parentIndex][1]) this.swap(index, parentIndex)
else break
index = parentIndex
}
}
private sortDown(index: number) {
let leftIndex: number, rightIndex: number, target: number
while (index < this.data.length) {
leftIndex = (index << 1) + 1
rightIndex = (index << 1) + 2
target = index
if (leftIndex < this.data.length && this.data[leftIndex][1] > this.data[target][1]) target = leftIndex
if (rightIndex < this.data.length && this.data[rightIndex][1] > this.data[target][1]) target = rightIndex
if (target === index) break
this.swap(index, target)
index = target
}
}
private swap(i: number, j: number) {
[this.data[i], this.data[j]] = [this.data[j], this.data[i]]
}
}
class Twitter {
private time: number
private users: {[key: number]: {followees: any, tweets: [number, number][]}} // [tweetId, time]
private tweetHeap: TweetsHeap
constructor() {
this.users = {}
this.time = 0
this.tweetHeap = new TweetsHeap()
}
postTweet(userId: number, tweetId: number): void {
if (!this.users[userId]) this.users[userId] = {followees: new Set([userId]), tweets: []}
this.users[userId].tweets.push([tweetId, this.time++])
}
getNewsFeed(userId: number): number[] {
if (!this.users[userId]) this.users[userId] = {followees: new Set([userId]), tweets: []}
this.users[userId].followees.forEach(followee => this.users[followee]?.tweets.forEach(t => this.tweetHeap.push(t)))
const res: number[] = []
while (this.tweetHeap.size() && res.length < 10) res.push(this.tweetHeap.pop()[0])
this.tweetHeap.clear()
return res
}
follow(followerId: number, followeeId: number): void {
if (!this.users[followerId]) this.users[followerId] = {tweets: [], followees: new Set([followerId])}
this.users[followerId].followees.add(followeeId)
}
unfollow(followerId: number, followeeId: number): void {
this.users[followerId].followees.delete(followeeId)
}
}
结语
这个系列会坚持更新,感谢支持
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/TM_Godspeed/article/details/117356454
所属网站分类: 技术文章 > 博客
作者:大师兄
链接:http://www.qianduanheidong.com/blog/article/115802/ac60676dd6aa43d520ed/
来源:前端黑洞网
任何形式的转载都请注明出处,如有侵权 一经发现 必将追究其法律责任
昵称:
评论内容:(最多支持255个字符)
---无人问津也好,技不如人也罢,你都要试着安静下来,去做自己该做的事,而不是让内心的烦躁、焦虑,坏掉你本来就不多的热情和定力