
2021前端面试之JavaScript手写题(一)
发布于2021-05-30 07:39 阅读(1126) 评论(0) 点赞(10) 收藏(5)

1.call的实现
- 第一个参数为null或者undefined时,this指向全局对象window,值为原始值的指向该原始值的自动包装对象,如 String、Number、Boolean
- 为了避免函数名与上下文(context)的属性发生冲突,使用Symbol类型作为唯一值
- 将函数作为传入的上下文(context)属性执行
- 函数执行完成后删除该属性
- 返回执行结果
Function.prototype.myCall = function(context,...args){
let cxt = context || window;
//将当前被调用的方法定义在cxt.func上.(为了能以对象调用形式绑定this)
//新建一个唯一的Symbol变量避免重复
let func = Symbol()
cxt[func] = this;
args = args ? args : []
//以对象调用形式调用func,此时this指向cxt 也就是传入的需要绑定的this指向
const res = args.length > 0 ? cxt[func](...args) : cxt[func]();
//删除该方法,不然会对传入对象造成污染(添加该方法)
delete cxt[func];
return res;
}
2.apply的实现
- 前部分与call一样
- 第二个参数可以不传,但类型必须为数组或者类数组
Function.prototype.myApply = function(context,args = []){
let cxt = context || window;
//将当前被调用的方法定义在cxt.func上.(为了能以对象调用形式绑定this)
//新建一个唯一的Symbol变量避免重复
let func = Symbol()
cxt[func] = this;
//以对象调用形式调用func,此时this指向cxt 也就是传入的需要绑定的this指向
const res = args.length > 0 ? cxt[func](...args) : cxt[func]();
delete cxt[func];
return res;
}
3.bind的实现
需要考虑:
- bind() 除了 this 外,还可传入多个参数;
- bind 创建的新函数可能传入多个参数;
- 新函数可能被当做构造函数调用;
- 函数可能有返回值;
实现方法:
- bind 方法不会立即执行,需要返回一个待执行的函数;(闭包)
- 实现作用域绑定(apply)
- 参数传递(apply 的数组传参)
- 当作为构造函数的时候,进行原型继承
Function.prototype.myBind = function (context, ...args) {
//新建一个变量赋值为this,表示当前函数
const fn = this
//判断有没有传参进来,若为空则赋值[]
args = args ? args : []
//返回一个newFn函数,在里面调用fn
return function newFn(...newFnArgs) {
if (this instanceof newFn) {
return new fn(...args, ...newFnArgs)
}
return fn.apply(context, [...args,...newFnArgs])
}
}
测试
let name = '小王',age =17;
let obj = {
name:'小张',
age: this.age,
myFun: function(from,to){
console.log(this.name + ' 年龄 ' + this.age+'来自 '+from+'去往'+ to)
}
}
let db = {
name: '德玛',
age: 99
}
//结果
obj.myFun.myCall(db,'成都','上海'); // 德玛 年龄 99 来自 成都去往上海
obj.myFun.myApply(db,['成都','上海']); // 德玛 年龄 99 来自 成都去往上海
obj.myFun.myBind(db,'成都','上海')(); // 德玛 年龄 99 来自 成都去往上海
obj.myFun.myBind(db,['成都','上海'])(); // 德玛 年龄 99 来自 成都, 上海去往 undefined
4.寄生式组合继承
function Person(obj) {
this.name = obj.name
this.age = obj.age
}
Person.prototype.add = function(value){
console.log(value)
}
var p1 = new Person({name:"番茄", age: 18})
function Person1(obj) {
Person.call(this, obj)
this.sex = obj.sex
}
// 这一步是继承的关键
Person1.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);
Person1.prototype.constructor = Person1;
Person1.prototype.play = function(value){
console.log(value)
}
var p2 = new Person1({name:"鸡蛋", age: 118, sex: "男"})
5.ES6继承
//class 相当于es5中构造函数
//class中定义方法时,前后不能加function,全部定义在class的protopyte属性中
//class中定义的所有方法是不可枚举的
//class中只能定义方法,不能定义对象,变量等
//class和方法内默认都是严格模式
//es5中constructor为隐式属性
class People{
constructor(name='wang',age='27'){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
eat(){
console.log(`${this.name} ${this.age} eat food`)
}
}
//继承父类
class Woman extends People{
constructor(name = 'ren',age = '27'){
//继承父类属性
super(name, age);
}
eat(){
//继承父类方法
super.eat()
}
}
let wonmanObj=new Woman('xiaoxiami');
wonmanObj.eat();
//es5继承先创建子类的实例对象,然后再将父类的方法添加到this上(Parent.apply(this))。
//es6继承是使用关键字super先创建父类的实例对象this,最后在子类class中修改this。
6.new的实现
- 一个继承自 Foo.prototype 的新对象被创建。
- 使用指定的参数调用构造函数 Foo,并将 this 绑定到新创建的对象。new Foo 等同于 new Foo(),也就是没有指定参数列表,Foo 不带任何参数调用的情况。
- 由构造函数返回的对象就是 new 表达式的结果。如果构造函数没有显式返回一个对象,则使用步骤1创建的对象。
- 一般情况下,构造函数不返回值,但是用户可以选择主动返回对象,来覆盖正常的对象创建步骤
function Ctor(){
....
}
function myNew(ctor,...args){
if(typeof ctor !== 'function'){
throw 'myNew function the first param must be a function';
}
var newObj = Object.create(ctor.prototype); //创建一个继承自ctor.prototype的新对象
var ctorReturnResult = ctor.apply(newObj, args); //将构造函数ctor的this绑定到newObj中
var isObject = typeof ctorReturnResult === 'object' && ctorReturnResult !== null;
var isFunction = typeof ctorReturnResult === 'function';
if(isObject || isFunction){
return ctorReturnResult;
}
return newObj;
}
let c = myNew(Ctor);
7.instanceof的实现
- instanceof 是用来判断A是否为B的实例,表达式为:A instanceof B,如果A是B的实例,则返回true,否则返回false。
- instanceof 运算符用来测试一个对象在其原型链中是否存在一个构造函数的 prototype 属性。
- 不能检测基本数据类型,在原型链上的结果未必准确,不能检测null,undefined
- 实现:遍历左边变量的原型链,直到找到右边变量的 prototype,如果没有找到,返回 false
function myInstanceOf(a,b){
let left = a.__proto__;
let right = b.prototype;
while(true){
if(left == null){
return false
}
if(left == right){
return true
}
left = left.__proto__
}
}
//instanceof 运算符用于判断构造函数的 prototype 属性是否出现在对象的原型链中的任何位置。
function myInstanceof(left, right) {
let proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(left), // 获取对象的原型
prototype = right.prototype; // 获取构造函数的 prototype 对象
// 判断构造函数的 prototype 对象是否在对象的原型链上
while (true) {
if (!proto) return false;
if (proto === prototype) return true;
proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(proto);
}
}
8.Object.create()的实现
-
MDN文档
-
Object.create()会将参数对象作为一个新创建的空对象的原型, 并返回这个空对象
//简略版
function myCreate(obj){
// 新声明一个函数
function C(){};
// 将函数的原型指向obj
C.prototype = obj;
// 返回这个函数的实力化对象
return new C()
}
//官方版Polyfill
if (typeof Object.create !== "function") {
Object.create = function (proto, propertiesObject) {
if (typeof proto !== 'object' && typeof proto !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError('Object prototype may only be an Object: ' + proto);
} else if (proto === null) {
throw new Error("This browser's implementation of Object.create is a shim and doesn't support 'null' as the first argument.");
}
if (typeof propertiesObject !== 'undefined') throw new Error("This browser's implementation of Object.create is a shim and doesn't support a second argument.");
function F() {}
F.prototype = proto;
return new F();
};
}
9.实现 Object.assign
Object.assign2 = function(target, ...source) {
if (target == null) {
throw new TypeError('Cannot convert undefined or null to object')
}
let ret = Object(target)
source.forEach(function(obj) {
if (obj != null) {
for (let key in obj) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
ret[key] = obj[key]
}
}
}
})
return ret
}
10.Promise的实现
实现 Promise 需要完全读懂 Promise A+ 规范,不过从总体的实现上看,有如下几个点需要考虑到:
- Promise本质是一个状态机,且状态只能为以下三种:Pending(等待态)、Fulfilled(执行态)、Rejected(拒绝态),状态的变更是单向的,只能从Pending -> Fulfilled 或 Pending -> Rejected,状态变更不可逆
- then 需要支持链式调用
class Promise {
callbacks = [];
state = 'pending';//增加状态
value = null;//保存结果
constructor(fn) {
fn(this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this));
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
this._handle({
onFulfilled: onFulfilled || null,
onRejected: onRejected || null,
resolve: resolve,
reject: reject
});
});
}
_handle(callback) {
if (this.state === 'pending') {
this.callbacks.push(callback);
return;
}
let cb = this.state === 'fulfilled' ? callback.onFulfilled : callback.onRejected;
if (!cb) {//如果then中没有传递任何东西
cb = this.state === 'fulfilled' ? callback.resolve : callback.reject;
cb(this.value);
return;
}
let ret = cb(this.value);
cb = this.state === 'fulfilled' ? callback.resolve : callback.reject;
cb(ret);
}
_resolve(value) {
if (value && (typeof value === 'object' || typeof value === 'function')) {
var then = value.then;
if (typeof then === 'function') {
then.call(value, this._resolve.bind(this), this._reject.bind(this));
return;
}
}
this.state = 'fulfilled';//改变状态
this.value = value;//保存结果
this.callbacks.forEach(callback => this._handle(callback));
}
_reject(error) {
this.state = 'rejected';
this.value = error;
this.callbacks.forEach(callback => this._handle(callback));
}
}
Promise.resolve
- Promsie.resolve(value) 可以将任何值转成值为 value 状态是 fulfilled 的 Promise,但如果传入的值本身是 Promise 则会原样返回它。
Promise.resolve(value) {
if (value && value instanceof Promise) {
return value;
} else if (value && typeof value === 'object' && typeof value.then === 'function') {
let then = value.then;
return new Promise(resolve => {
then(resolve);
});
} else if (value) {
return new Promise(resolve => resolve(value));
} else {
return new Promise(resolve => resolve());
}
}
Promise.reject
- 和 Promise.resolve() 类似,Promise.reject() 会实例化一个 rejected 状态的 Promise。但与 Promise.resolve() 不同的是,如果给 Promise.reject() 传递一个 Promise 对象,则这个对象会成为新 Promise 的值。
Promise.reject = function(reason) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => reject(reason))
}
Promise.all
- 传入的所有 Promsie 都是 fulfilled,则返回由他们的值组成的,状态为 fulfilled 的新 Promise;
- 只要有一个 Promise 是 rejected,则返回 rejected 状态的新 Promsie,且它的值是第一个 rejected 的 Promise 的值;
- 只要有一个 Promise 是 pending,则返回一个 pending 状态的新 Promise;
Promise.all = function(promiseArr) {
let index = 0, result = []
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
promiseArr.forEach((p, i) => {
Promise.resolve(p).then(val => {
index++
result[i] = val
if (index === promiseArr.length) {
resolve(result)
}
}, err => {
reject(err)
})
})
})
}
Promise.race
- Promise.race 会返回一个由所有可迭代实例中第一个 fulfilled 或 rejected 的实例包装后的新实例。
Promise.race = function(promiseArr) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
promiseArr.forEach(p => {
Promise.resolve(p).then(val => {
resolve(val)
}, err => {
rejecte(err)
})
})
})
}
11.Ajax的实现
function ajax(url,method,body,headers){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
let req = new XMLHttpRequest();
req.open(methods,url);
for(let key in headers){
req.setRequestHeader(key,headers[key])
}
req.onreadystatechange(()=>{
if(req.readystate == 4){
if(req.status >= '200' && req.status <= 300){
resolve(req.responeText)
}else{
reject(req)
}
}
})
req.send(body)
})
}
总结一下
面试前要精心做好准备,简历上写的知识点和原理都需要准备好,项目上多想想难点和亮点,这是面试时能和别人不一样的地方。
还有就是表现出自己的谦虚好学,以及对于未来持续进阶的规划,企业招人更偏爱稳定的人。
万事开头难,但是程序员这一条路坚持几年后发展空间还是非常大的,一切重在坚持。
为了帮助大家更好更高效的准备面试,特别整理了《前端工程师面试手册》电子稿文件。
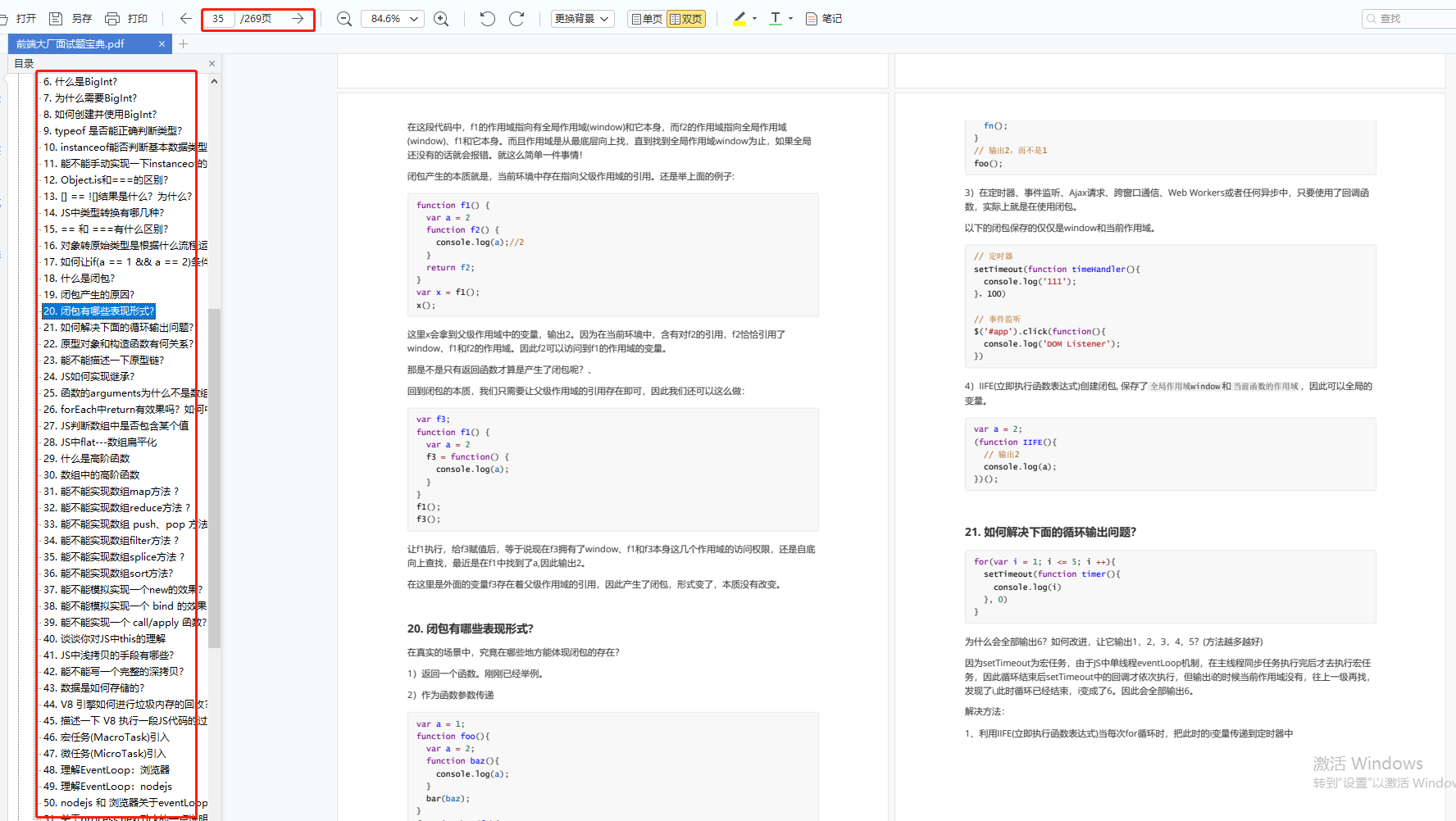
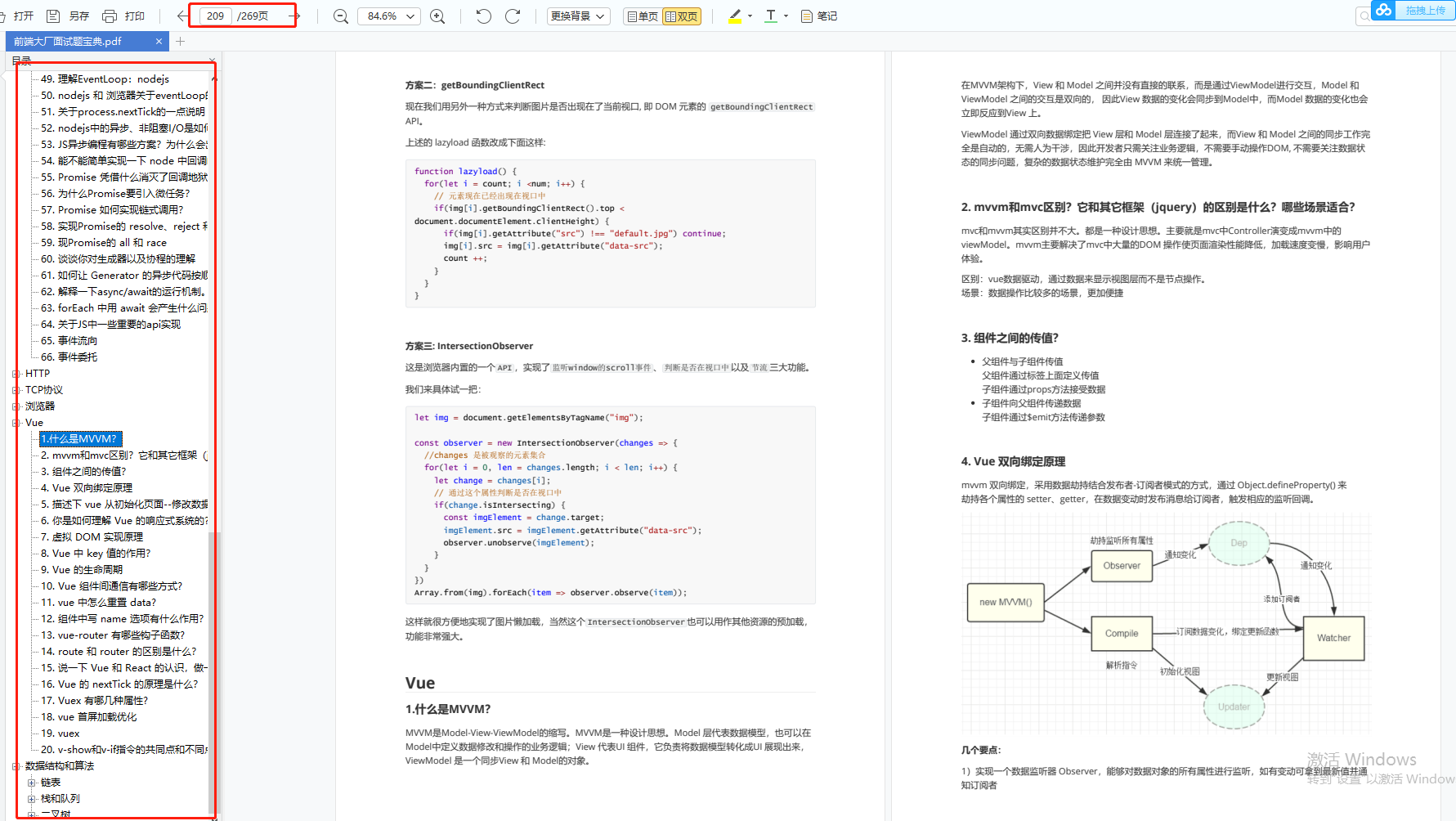
前端面试题汇总
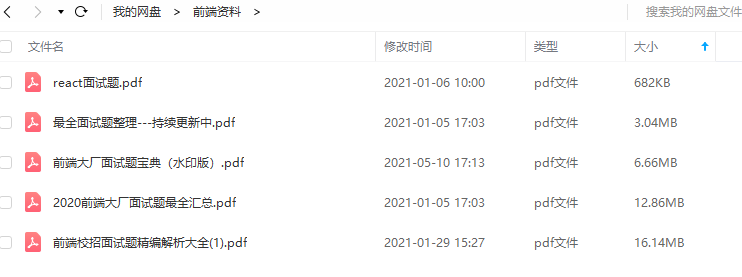
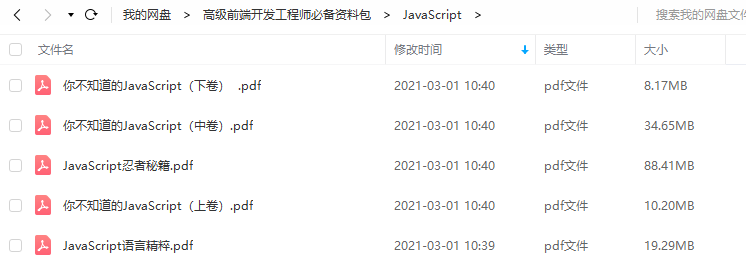
JavaScript
性能
linux
前端资料汇总
完整版PDF资料免费分享,只需你点赞支持,动动手指点击此处就可免费领取了。
前端工程师岗位缺口一直很大,符合岗位要求的人越来越少,所以学习前端的小伙伴要注意了,一定要把技能学到扎实,做有含金量的项目,这样在找工作的时候无论遇到什么情况,问题都不会大。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/hugo233/article/details/117375154
所属网站分类: 技术文章 > 博客
作者:Bhbvhbbgg
链接:http://www.qianduanheidong.com/blog/article/115762/c91addfada22e9462be7/
来源:前端黑洞网
任何形式的转载都请注明出处,如有侵权 一经发现 必将追究其法律责任
昵称:
评论内容:(最多支持255个字符)
---无人问津也好,技不如人也罢,你都要试着安静下来,去做自己该做的事,而不是让内心的烦躁、焦虑,坏掉你本来就不多的热情和定力